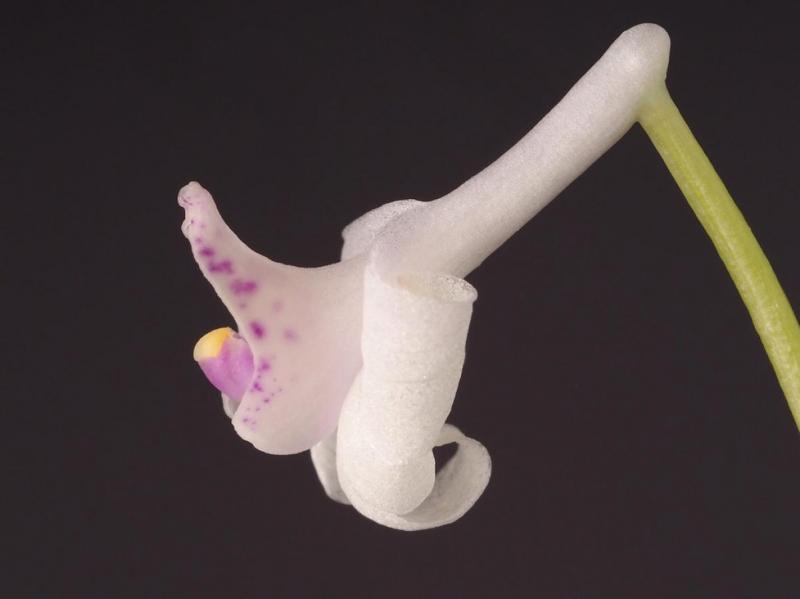
Anthogonium gracile
Also known as: The Slender Anthogonium or Anthogonium griffithii Anthogonium corydaloides In Thailand - Wan phrao in the subfamily: Epidendroideae
Native to: Cambodia Guizhou - China Nepal
General Information
The Slender Anthogonium is a cool to hot growing epiphytic or terrestrial orchid belonging to the sub family Epidendroideae native to Cambodia, China and Nepal.
Plant Description
Grows to 37cm. Each new growth has numerous elliptic leaves that grow to 3.5-37cm long. Pseudobulbs grow to 2cm. The plant tends to climb or sprawl with each new growth
Substrate(s)
- Coarse
- Charcoal
- Spaghnum Moss
- Perlite
- Sand
Care Notes
This orchid goes into a dormancy phase during winter, during this phase it is best not to provide water unless the plant is starting to look thirsty. The lack of water increases the chance of flowering in spring, and also reduces the likelihood of any rot forming. Do not resume watering until new growth has appeared and is growing strongly.
Often a period of intense growth occurs after dormancy. During this time the amount of light, water and fertiliser the plant receives will directly impact the amount of growth that occurs during this time, and in the case of seedlings, will reduce the time required to reach maturity.
It's recommended to heavily reduce the water amount at the middle to end of autumn to trigger dormancy. Leaves on older bulbs will begin to drop during this time while the newer bulbs continue to mature until terminal leaves appear at the tip of the pseudobulbs.
Repotting can be done any time of the year though it's best to do it in early spring when new growth is appearing as this also means new roots will appear to help the plant anchor into the new media and offset any damage to established roots during the repotting process.
Climate
Grows at low to high elevations. Rainfall ranges from 5mm to 259mm per day, heaviest in July and lightest in January. Humidity ranges from 61% to 79%, highest in August and lowest in April. Temperature ranges from 4C to 27C, highest in May (17C to 27C) and lowest in January (4C to 16C).
Fertiliser
dormant-medium-demand-orchid Use balanced fertiliser year round. Fertiliser can be applied heavily year round. Apply fertiliser regularly at half strength year round. Use a high Nitrogen fertiliser during Spring and Summer. Use a high Phosphorous fertiliser during Summer.
Potting
These plants can be sensitive to repotting though should not require repotting regularly. Repotting should be done when the mix has broken down to the point that it doesn't absorb water or holds onto water for far too long, usually the plant shows a decline in growth as well. Repotting is best done after the growing season when the plant has died back.
The mix should be free draining, with a blend of 30% inorganic ingredients such as coarse sand, gravel or perlite, mixed in with about 70% organic ingredients such as peat, leaf litter or decomposed bark. Avoid commercial potting mixes as they can vary wildly and may contain "wetting agents" that can hold onto water for loo long, causing rotting and stunted growth.
Use water retentive media such as moss to prevent roots from drying out quickly Repotting is best done annually.