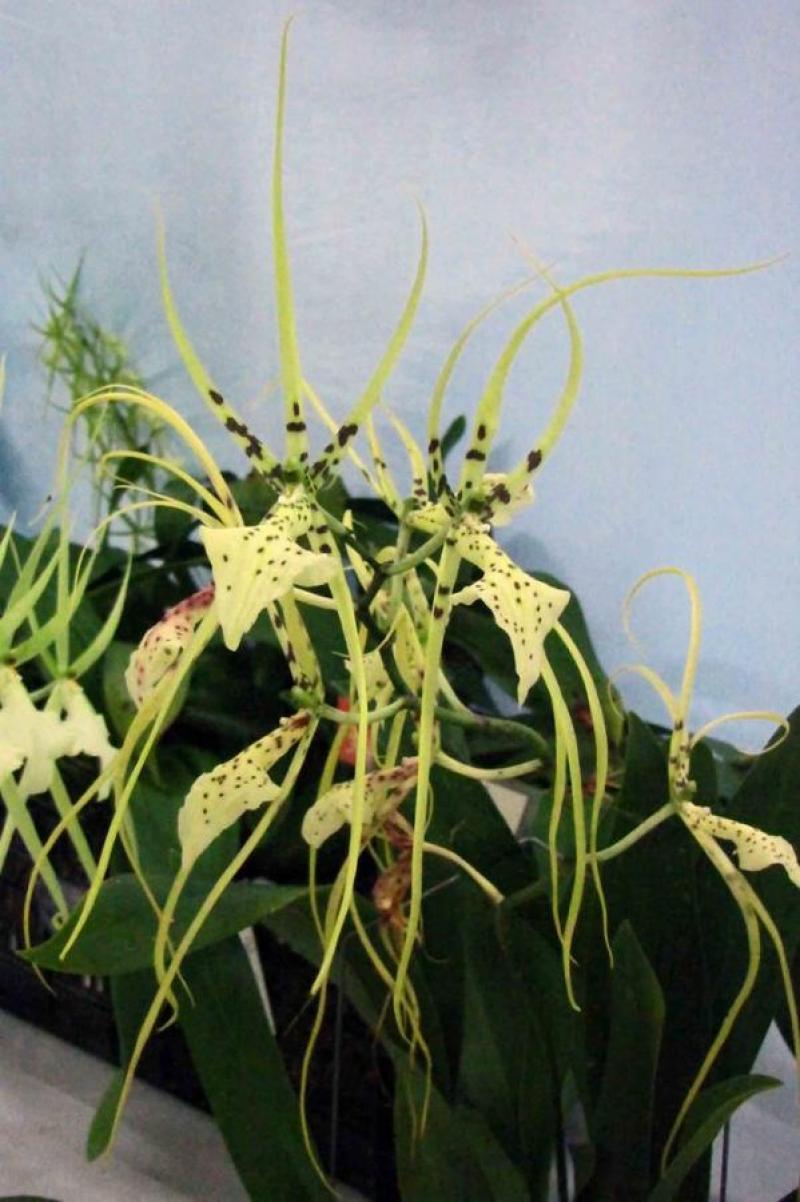
Brassia wageneri
Also known as: Wagner's Brassia or Brassia bicolor Brassia cryptophthalma in the subfamily: Epidendroideae
Native to: Departamento del Huila - Colombia Junin - Peru
General Information
Wagner's Brassia is a small to medium sized sympodial cool to warm growing epiphytic orchid belonging to the sub family Epidendroideae native to Colombia and Peru. It is named after the Germna Orchid Collector in Venezuela in the 19th century.
Plant Description
Sympodial. Grows to 34cm. Each new growth has numerous elliptic oblong shaped leaves that grow to 5-25cm long. Pseudobulbs grow to 3-15cm
Flowers
Numerous blossoms appear during Summer and Autumn
Blooming Season
- Autumn
- Summer
Substrate(s)
- Coarse
- Bark
- Spaghnum Moss
- Perlite
Care Notes
This orchid goes into a dormancy phase during winter, during this phase it is best not to provide water unless the plant is starting to look thirsty. The lack of water increases the chance of flowering in spring, and also reduces the likelihood of any rot forming. Do not resume watering until new growth has appeared and is growing strongly.
Often a period of intense growth occurs after dormancy. During this time the amount of light, water and fertiliser the plant receives will directly impact the amount of growth that occurs during this time, and in the case of seedlings, will reduce the time required to reach maturity.
It's recommended to heavily reduce the water amount at the middle to end of autumn to trigger dormancy. Leaves on older bulbs will begin to drop during this time while the newer bulbs continue to mature until terminal leaves appear at the tip of the pseudobulbs.
Repotting can be done any time of the year though it's best to do it in early spring when new growth is appearing as this also means new roots will appear to help the plant anchor into the new media and offset any damage to established roots during the repotting process.
Climate
Grows at low to high elevations. Rainfall ranges from 114mm to 632mm per day, heaviest in May and lightest in December. Humidity ranges from 76% to 81%, highest in July and lowest in February. Temperature ranges from 16C to 29C, highest in February (17C to 29C) and lowest in January (16C to 28C).
Watering
These orchids prefer a constant supply of moisture, with a slight drying out between waterings. Saucers can be placed under pots to retain moisture during hot weather, however the saucers should be removed or let to dry every 1-2 weeks to prevent rot. Keep an eye on the plant especially in hot weather and look for cues of under/overwatering and adjust accordingly.
Keep moisture levels up during hot weather as the plant is prone to dehydrationFertiliser
dormant-medium-demand-orchid Use balanced fertiliser year round. Be sure to flush out excess fertiliser by running water through the media regularly year round. Apply fertiliser regularly at half strength year round. Use a low Nitrogen fertiliser during Winter. Use a high Phosphorous fertiliser during Winter.
Potting
These plants are quite forgiving and will do well repotted ever 2-3 years. The mix should be coarse, well draining, and allow space for air to move and for roots to grow.
Alternatively, these plants will also do well mounted to tree fern or cork slabs, or mounted to trees.
Best time for repotting or mounting the orchids is the end of winter when new growths start to appear. Avoid repotting during hot weather,
Use water retentive media such as moss to prevent roots from drying out quickly Repotting is best done annually.