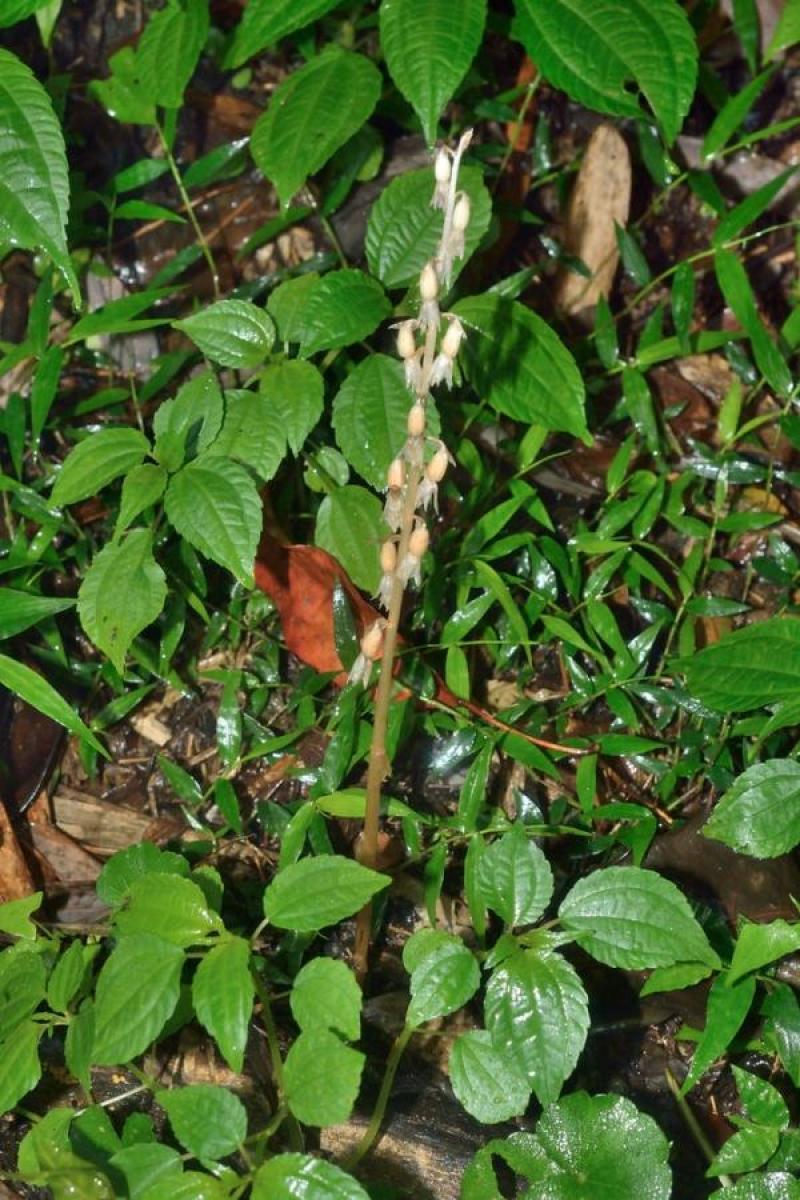
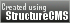
Epipogium roseum
Also known as: The Rose Epipogium or Stereosandra schinziana Podanthera pallida Ceratopsis rosea Epipogium indicum Epipogium rolfei Epipogium dentilabellum Epipogium kassnerianum Epipogium sessanum Epipogium africanus Galera kusukusensis Epipogium sinicum Epipogium guilfoylii Gastrodia schinziana Epipogium kusukusense Galera rolfei Epipogium makinoanum Epipogium nutans Galera rosea Epipogium nutans var. celebicus Epipogium pooneranthum Galera nutans Epipogium tuberosum in Australia - The Ghost Orchid or The Leafless Nodding Orchid in the subfamily: Epidendroideae
Native to: Angola Bhutan Cameroon Fiji Ghana India Japan Kenya Malawi Malaysia New Caledonia Nigeria Pakistan Thailand Uganda
General Information
The Rose Epipogium is a cool to hot growing terrestrial orchid belonging to the sub family Epidendroideae native to Angola, Bhutan, Cameroon, Fiji, Ghana, India, Japan, Kenya, Malawi, Malaysia, New Caledonia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Thailand, and Uganda.
Plant Description
Each new growth has numerous thick erect leaves
Flowers
Numerous blossoms appear during Summer and Spring
Blooming Season
- Spring
- Summer
Care Notes
These orchids live on the forest floor and keep tubers to store energy and nutrients during dormancy and poor weather. They are generally quite forgiving and usually thrive on neglect, as long as it's the type of neglect where they are forgotten to be watered or fertilised, as overwatering can cause rot, and excessive fertilisers can affect the fine root system.
They are quite forgiving when it comes to light and environmental conditions, as long as they have enough moisture in the soil to keep going. Damage to leaves from overexposure to light or dry conditions has no long term implications as the plant will withdraw back to the tuber and be replaced with a new plant in the next season. Just be sure not to overwater damaged plants as they will rot.
They will enter a dormancy phase where leaves are shedded the plant withdraws back to the ground. During dormancy tubers can be removed from the soil, kept in a dry cool place if required, replanting when new roots appear. However, most plants will do better if not disturbed, and replanting late can set back the plant and reduce the likelihood of flowering in the following year.
In many areas these can be grown in the garden, needing little maintenance.
Climate
Grows at low to high elevations.
Fertiliser
These plants do well with slow release fertiliser at the rate of 2-3 pellets per cup (250ml) of media. Additional fertiliser during the growth period may be beneficial, but not necessary.
Potting
These plants can be sensitive to repotting though should not require repotting regularly. Repotting should be done when the mix has broken down to the point that it doesn't absorb water or holds onto water for far too long, usually the plant shows a decline in growth as well.
The mix should be free draining, with a blend of 30% inorganic ingredients such as coarse sand, gravel or perlite, mixed in with about 70% organic ingredients such as peat, leaf litter or decomposed bark. Avoid commercial potting mixes as they can vary wildly and may contain "wetting agents" that can hold onto water for loo long, causing rotting and stunted growth.