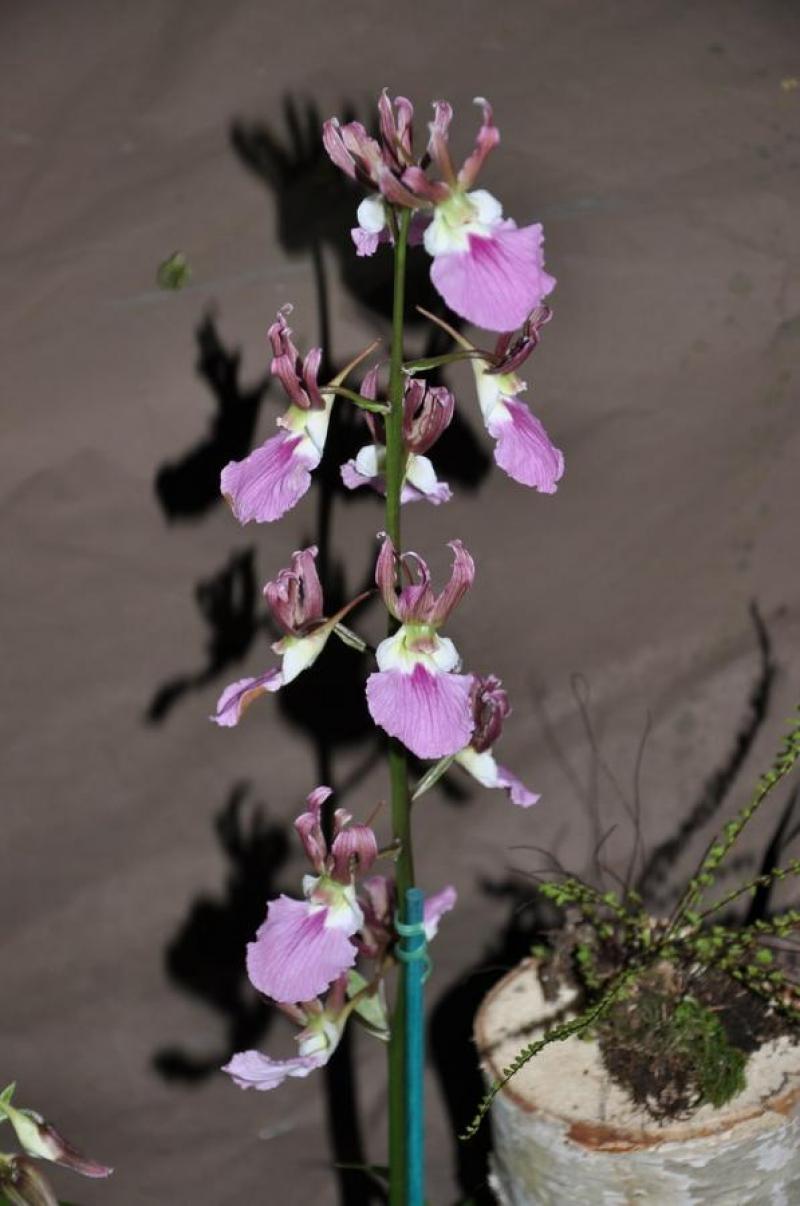
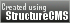
Eulophia guineensis
Also known as: The Guinea Eulophia or Saccolabium abyssinicum Eulophia guineensis var. purpurata Eulophia quartiniana Galeandra quartiniana Eulophia guineensis var. kibilana Eulophia congoensis Eulophia guineensis var. tisserantii in the subfamily: Epidendroideae
Native to: Angola Congo Gambia Kenya Nigeria Uganda
General Information
The Guinea Eulophia is a large sympodial warm growing terrestrial orchid belonging to the sub family Epidendroideae native to Angola, Congo, Gambia, Kenya, Nigeria, and Uganda.
Plant Description
Sympodial. Grows to 30-65cm. Each new growth has numerous erect elliptic leaves that grow to 3-35cm long. Pseudobulbs grow to 2-5cm
Flowers
Numerous fragrant blossoms appear
Fragrance
The orchid is fragrant.
Substrate(s)
- Coarse
- Bark
- Charcoal
- Treefern
- Perlite
- Sand
Care Notes
These orchids live on the forest floor, often in dead leaves or humus, yet still have the organs that would allow them to store water given unpredictable or intermittent weather conditions. They require some moisture to always be present in the soil, but not much. Water when the soil approaches dryness and don't let it dry out completely. Some growers place pots in saucers to retain water, but this may create an environment that is too wet, leading to rot.
In most areas these can be grown in the garden under trees or in sheltered locations, as long as they are reasonably protected from huge weather swings, excessive heat, and frost.
Fragrant:- IsFragrant
Climate
Grows at low to high elevations. Rainfall ranges from 15mm to 165mm per day, heaviest in May and lightest in January. Humidity ranges from 49% to 75%, highest in July and lowest in January. Temperature ranges from 11C to 28C, highest in February (13C to 28C) and lowest in January (11C to 23C).
Fertiliser
Apply liquid based fertiliser per recommended directions. They can benefit from a high phosphate fertiliser leading up to flowering season, followed by a high nitrogen fertiliser when new growth appears, and a balanced fertiliser in other times. These orchids can also tolerate slow release fertiliser applied 1-2 pellets per cup (250ml) of media.
Use balanced fertiliser year round. Apply fertiliser regularly at half strength year round. Use a high Nitrogen fertiliser during Spring and Summer. Use a high Phosphorous fertiliser during Summer.Potting
These plants can be sensitive to repotting though should not require repotting regularly. Repotting should be done when the mix has broken down to the point that it doesn't absorb water or holds onto water for far too long, usually the plant shows a decline in growth as well.
The mix should be free draining, with a blend of 30% inorganic ingredients such as coarse sand, gravel or perlite, mixed in with about 70% organic ingredients such as peat, leaf litter or decomposed bark. Avoid commercial potting mixes as they can vary wildly and may contain "wetting agents" that can hold onto water for loo long, causing rotting and stunted growth.
This plant does well mounted. Repotting is best done annually.