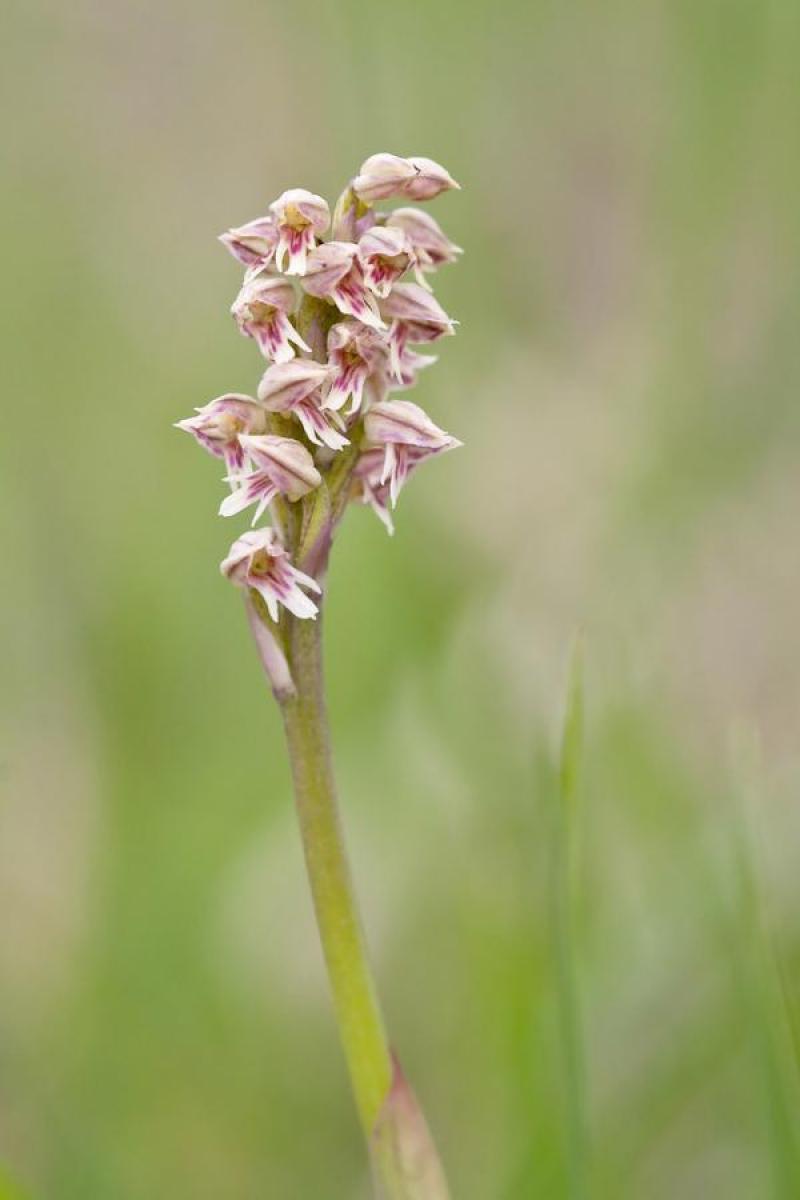
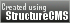
Neotinea maculata
Also known as: The Spotted Neotina or Orchis imbecilla Orchis ustulata var. ecalcarata Orchis intacta Orchis atlantica Ophrys secundiflora Orchis secundiflora Peristylus densiflorus Peristylus maculatus Orchis sagittata Satyrium atlanticum Peristylus atlanticus Orchis ecalcarata Tinea intacta Tinea cylindrica Aceras densiflorum Aceras maculatum Aceras intactum Aceras secundiflorum Aceras densiflorum f. bifidum Aceras densiflorum f. tridentatum Neotinea intacta Neotinea maculata f. luteola Coeloglossum densiflorum Neotinea intacta f. luteola Neotinea maculata f. alba Aceras vayredae Neotinea intacta f. tridentata Himantoglossum parviflorum Ophrys densiflora Himantoglossum secundiflorum Neotinea intacta var. bifida Neotinea intacta f. bifida Neotinea intacta var. tridentata Neotinea maculata var. stricta Habenaria intacta in the subfamily: Orchidoideae
Native to: Greece
General Information
The Spotted Neotina is a cold to cool growing terrestrial orchid belonging to the sub family Orchidoideae native to Greece.
Flowers
Numerous blossoms appear during Winter and Spring
Blooming Season
- Spring
- Winter
Care Notes
These orchids grow on the forest floor so are used to rich soil containing plenty of organic matter that is always moist (but not always wet), and prefer constant conditions in terms of humidity, temperature and water supply. They may not be as forgiving as epiphytes in regards to sudden changes in growing conditions so it is wise to ease them into new conditions over a the space of a few days, and repot as infrequently as possible.
Keep an eye on the plants condition regularly as they can decline suddenly if the conditions are not just right. It is more important to keep water supply constant rather than frequent - overwatering often causes rot which can quickly set in, especially in warmer conditions.
These can be grown in shady, moist areas in the garden, supplied they have protection from abrupt changes caused by the elements, e.g. dry winds, frost etc. Being grown around companion plants such as ferns and bromeliads will help build and retain the humidity they require throughout the year.
Fertiliser
These plants do well with slow release fertiliser at the rate of 2-3 pellets per cup (250ml) of media. Additional fertiliser during the growth period may be beneficial, but not necessary.
Potting
These plants can be sensitive to repotting though should not require repotting regularly. Repotting should be done when the mix has broken down to the point that it doesn't absorb water or holds onto water for far too long, usually the plant shows a decline in growth as well.
The mix should be free draining, with a blend of 30% inorganic ingredients such as coarse sand, gravel or perlite, mixed in with about 70% organic ingredients such as peat, leaf litter or decomposed bark. Avoid commercial potting mixes as they can vary wildly and may contain "wetting agents" that can hold onto water for loo long, causing rotting and stunted growth.